Voicing
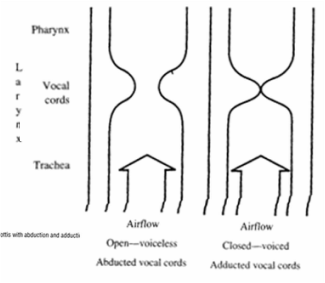
Voiceless SoundsVoiceless sounds are made by forcing air past the vocal cords without them vibrating.
|
How to tell if it is Voiced or Voiceless... |
Voiced SoundsVoiced sounds are created by forcing air past the vocal cords and causing them to vibrate.
|
Place of Articulation
|
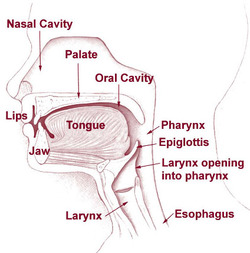
The place of articulation is where the airflow is restricted within the vocal tract.
There are 8 places of articulation within the vocal tract. Click each one to hear the sounds created there.
|
|
Manner of Articulation
Trills and flaps
Approximants
|
Manner of articulation discusses how airflow changes when trying to make a sound. Some of the different obstacles are listed below.
Stops
Fricatives
Affricates
Liquids
Glides
Clicks
|
Features Which Do Not Distinguish Phonemes
Syllabic versus
|
Stress versus
|
Aspiration versus Nonaspiration
|
Why it is important for ELL teachers to understand the characteristics of speech.

- As a classroom teacher,knowing the parts and production of speech will allow you to teach them better.
- Teachers can become allies in assisting student diagnose and correct speech errors which leads to great confidence in students.
- By understanding common errors, a teacher can more readily provide support and training for a student to help them overcome the issue.